The winter of 2025 marked a turning point. Reducing heat loss in homes during winter has shifted from a desire to an urgent necessity for most homeowners. According to the International Energy Agency, about 30% of the energy used for heating literally escapes through poor insulation, equivalent to wasting $800–$1,200 annually.
Reducing heat loss in a home is a matter of economic calculation. A comprehensive approach to energy conservation in a private home includes external and internal insulation, sealing window openings, and upgrading ventilation systems. According to the EU Directive on the Energy Performance of Buildings, by 2050, all buildings must achieve full decarbonization—a process that, like an avalanche, is unstoppable.
"Quality insulation is like a thermos for your home. Invest once in proper insulation, and you save for decades, with the house running like a Swiss watch." — Michael Anderson, energy efficiency expert
In my work with private clients, I’ve noticed a pattern. Homeowners often buy powerful boilers first, then are shocked by astronomical bills. It’s crucial to understand that tackling heat loss in winter should start with a detailed analysis of all the building’s weak points.
How and Where a Home Loses Heat: Analyzing Key Sources
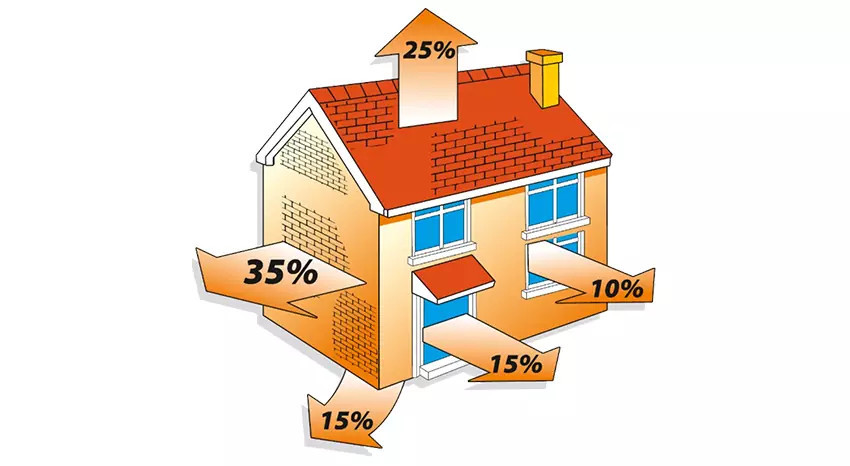 Where does heat escape from a home? The numbers vary depending on the year of construction and insulation quality. European standard EN 13829 sets the air exchange rate at 50 Pa to no more than 3 h⁻¹ for energy-efficient buildings—a sort of breathing membrane, but strictly controlled.
Where does heat escape from a home? The numbers vary depending on the year of construction and insulation quality. European standard EN 13829 sets the air exchange rate at 50 Pa to no more than 3 h⁻¹ for energy-efficient buildings—a sort of breathing membrane, but strictly controlled.
A detailed analysis of the main sources of heat loss helps prioritize measures for heat retention in a home.
| Source of Heat Loss | Older Homes (%) | Modern Homes (%) | Solution | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows and Doors | 35-50% | 15-25% | Energy-saving glazing | $400-800 |
| Walls | 25-40% | 35-45% | External facade insulation | $300-600 |
| Roof and Ceiling | 15-25% | 20-30% | Ceiling insulation | $200-400 |
| Floor | 10-15% | 10-15% | Floor insulation in private homes | $150-300 |
| Ventilation | 5-10% | 15-25% | Chimney heat recovery | $100-250 |
This data clearly illustrates the differences in heat loss. Comprehensive methods to reduce heat loss can cut heating costs by 40–60%, depending on the building’s initial condition and the quality of the work.
Detailed Analysis of Heat Loss Through Structural Elements
.jpg) For maximum energy-saving efficiency, it’s essential to analyze the contribution of each structural element to overall heat loss.
For maximum energy-saving efficiency, it’s essential to analyze the contribution of each structural element to overall heat loss.
Walls: Hidden Enemies of Energy Efficiency
Thermal bridges in a home act like heat vacuums. Last season, a thermographic survey on one project revealed leaks in the most unexpected places—where insulation work seemed flawless.
The dew point in walls shifts unpredictably, creating conditions for condensation and gradual structural damage. According to European standard EN ISO 13788, dew point calculations must account for regional climate conditions and material thermal conductivity.
| Problem Type | Heat Loss (%) | Signs | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lack of Thermal Protection | 30-45% | Cold walls, condensation | External wall insulation |
| Thermal Bridges | 15-25% | Localized freezing | Thermal inserts, node insulation |
| Poor Installation | 10-20% | Gaps in insulation | Dismantling and reinstallation |
| Material Wear | 5-15% | Insulation settling | Purchase and replace insulation |
Identifying and addressing these issues is critical. Only then can normative thermal resistance levels be achieved, per international standards.
Windows and Doors: The First Line of Defense
 Insulating windows for winter requires a systematic approach. European standard EN 14351-1 sets strict requirements for window block energy efficiency—heat transfer coefficient Uw no higher than 0.8–1.0 W/(m²·K) for modern systems, and even stricter for passive houses, up to 0.8 W/(m²·K).
Insulating windows for winter requires a systematic approach. European standard EN 14351-1 sets strict requirements for window block energy efficiency—heat transfer coefficient Uw no higher than 0.8–1.0 W/(m²·K) for modern systems, and even stricter for passive houses, up to 0.8 W/(m²·K).
"Warm windows for a home aren’t a luxury—they’re a necessity. Choosing the right glazing cuts heat loss through windows by an impressive 70%." — Anna Müller, thermal engineering expert
Modern methods include several proven solutions. Balcony glazing insulation is particularly relevant in multi-story buildings:
- Replacing old windows with energy-saving glazing with low-emissivity coating
- Sealing window openings with special sealants and mounting foam
- Installing heat-reflective window film for additional insulation
- Installing double doors to combat cold in private buildings
- Updating window sealing gaskets every 5–7 years
Applying these technologies together ensures compliance with European standards, resulting in significant reductions in heating costs.
Floor and Ceiling: The Top and Bottom of Energy Efficiency
.jpg) How to properly insulate a floor in a home? The choice depends on the foundation type and the presence of a basement. Given the building’s structural features, insulation work over unheated spaces requires special attention.
How to properly insulate a floor in a home? The choice depends on the foundation type and the presence of a basement. Given the building’s structural features, insulation work over unheated spaces requires special attention.
It’s well-known that warm air rises. Thus, ceiling insulation in a home is a priority for energy conservation. According to European studies on insulation materials, choosing the right insulation can reduce inefficient heat loss through the roof by an impressive 80%.
Thermal Protection Technologies: External and Internal Insulation
</tech stack img src="assets/images/blog/photo_445981.jpeg" alt="apartment insulation from the outside" width="800">How to properly insulate walls? There are two fundamentally different approaches. Standard EN 13162 details the characteristics of mineral wool insulation materials for construction applications.
Insulating walls internally with mineral wool is suitable for apartments in multi-story buildings. It’s not always feasible but sometimes the only option.
Given the building’s structural features, internal wall insulation requires a mandatory vapor barrier membrane to prevent condensation.
"External thermal protection is the gold standard of energy efficiency in construction. Internal insulation is a forced compromise when other options are technically unfeasible." — Jennifer Clark, architect-energy auditor
European external facade insulation technologies include three main systems:
- Ventilated facade insulation—creates a controlled air gap between the wall and cladding
- Wet facade—insulation is fixed to the wall and covered with plaster
- Three-layer wall—insulation material is placed between two walls during construction
Each system is time-tested and meets European quality standards. Durable protection against heat loss is guaranteed when technology is followed.
Insulation permeability plays a critical role in system longevity. Basalt mineral wool ensures an ideal temperature-humidity balance, while extruded polystyrene requires additional ventilation. Notably, polystyrene is a combustible material (groups G3–G4), limiting its use in high-rise buildings and requiring extra fire safety measures.
Energy-Saving Windows: Technologies and Solutions
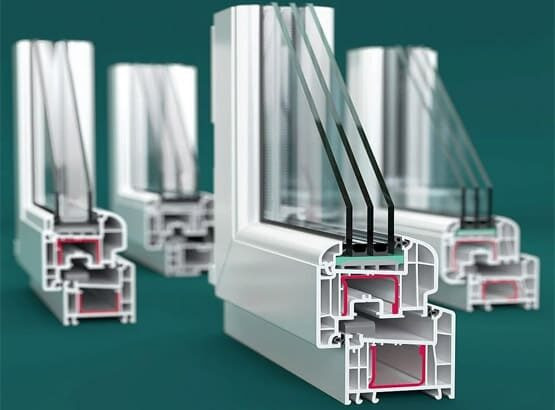 In practice, I often notice clients’ surprise. Replacing old windows with modern systems delivers immediate results—the home becomes quieter, warmer, and more comfortable.
In practice, I often notice clients’ surprise. Replacing old windows with modern systems delivers immediate results—the home becomes quieter, warmer, and more comfortable.
Installing energy-saving windows with triple glazing reduces heat loss by 70% compared to old wooden frames. Standard EN 673 defines precise methods for calculating heat transfer through glazing.
"In 2023, we replaced all windows in our 1980s home with energy-efficient triple glazing. Heating bills dropped from $180 to $110 per month in the first winter. The building became much quieter, and drafts near windows disappeared. The $8,000 investment will pay off in 4 years, and the comfort is priceless." — Sarah Johnson, homeowner from Minnesota
Insulating the front door includes installing double doors to combat cold and using modern sealants. Heat-reflective window film can further reduce heat loss through glazing by 10–15%.
Insulation Work: Floor and Ceiling
When performing insulation work on horizontal surfaces, different requirements for insulating floors and ceilings must be considered, driven by heat flow direction and operating conditions.
Features of Floor Thermal Protection
European standard EN 13163 sets strict requirements for extruded polystyrene used in floor insulation. Insulating floors in a private home above a basement requires moisture-resistant materials—extruded polystyrene or sprayed polyurethane foam yield excellent results.
Types of Ceiling Insulation
Properly executed ceiling thermal protection can reduce inefficient heat loss through upper structures by 60–80% with correct installation and operation. Material thermal conductivity must strictly match the climate zone—for northern regions, a 200–300 mm insulation layer is required per EN ISO 6946.
It’s critical to consider building energy efficiency classes when selecting insulation thickness. Achieving class A+ requires a thicker insulation layer and high-quality vapor barriers with a vapor permeability resistance of at least 100 m²·h·Pa/mg.
Heat Recovery Systems: Reclaiming Lost Heat
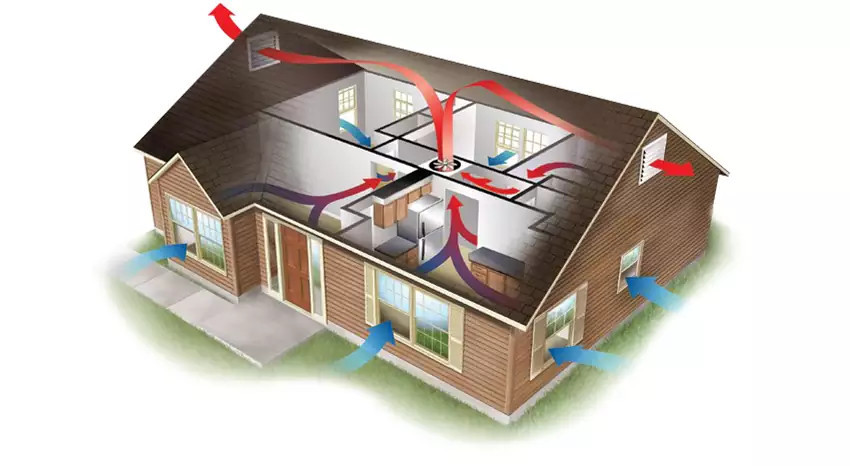 The efficiency of a heat recovery system directly depends on understanding the physical principles of heat exchange between supply and exhaust air streams.
The efficiency of a heat recovery system directly depends on understanding the physical principles of heat exchange between supply and exhaust air streams.
How Heat Recovery Units Work
What is heat recovery in construction? It’s a smart technology for reclaiming heat from exhaust air. Modern heat recovery units return up to 85–90% of heat in ideal operating conditions, which would otherwise be lost through ventilation. Standard EN 308 details the characteristics of heat exchangers for heat recovery.
Heat Recovery in Furnace Heating
In a recent project, installing a heat exchanger for a furnace in a country home increased the heating system’s efficiency by 25%. A chimney heat recovery unit captures heat from flue gases, which would otherwise escape into the atmosphere—like money down the drain.
"A heat recovery system is the lungs of your home. It provides fresh air without losing precious heat, acting as a smart energy filter." — Thomas Brown, climate systems engineer
Step-by-Step Plan for Improving Home Energy Efficiency
Effective heat retention in a home requires a systematic approach. Seasonal specificity of work is crucial.
| Stage | Season | Tasks | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | Spring | Order a thermographic survey, heat loss audit | 1–2 weeks |
| Planning | Summer | Select materials, contractors, prepare budget | 1 month |
| Main Work | Fall | Order facade insulation, window replacement | 2–4 months |
| Monitoring | Winter | Track expenses, adjust system | Ongoing |
Following this plan ensures maximum investment efficiency, resulting in significant energy savings in a private home.
DIY Methods to Reduce Heat Loss
Simple methods are accessible to every homeowner and don’t require specialists.
Preparatory Work Before Insulation
In practice, I often notice one mistake—homeowners start insulation work without proper preparation. The result is predictable:
- Cleaning surfaces of mold, fungus, and old coatings
- Checking the condition of load-bearing structures and fixing defects
- Ensuring access to work surfaces
- Preparing tools and protective equipment
DIY Solutions for Heat Conservation
- Insulating windows for winter with special films and sealants
- Sealing gaps and cracks with mounting foam or sealant
- Installing heat-reflective screens behind radiators
- Adjusting the heating system and installing thermostats
- Eliminating drafts in door openings
These measures can reduce heat loss by 15–25%. Costs are minimal—up to $200.
Common Insulation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Knowing typical errors saves time and money, preventing serious issues in the future.
| Mistake | Consequences | How to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Dew Point Calculation | Condensation, mold, structural damage | Calculate per EN ISO 13788 |
| Poor Vapor Barrier | Insulation dampening | Continuous vapor barrier contour |
| Skimping on Materials | Rapid wear, low efficiency | Purchase certified insulation materials |
| Improper Installation | Thermal bridges, loose fitting | Professional turnkey insulation installation |
Avoiding these mistakes is critical for achieving stated energy efficiency metrics. It’s better to spend more time planning than redoing the work.
Heat Loss Diagnostics: Modern Methods
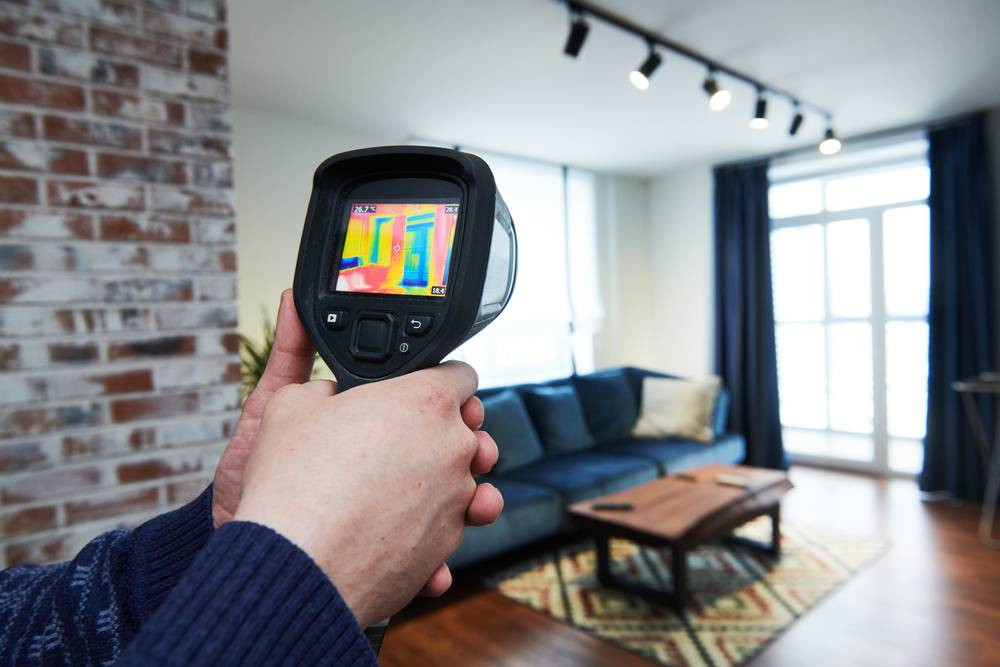 How to professionally check a home’s heat loss? The need for a home thermal imager becomes clear after the first survey. European standard EN 13187 details thermographic control methods for the thermal properties of building envelopes.
How to professionally check a home’s heat loss? The need for a home thermal imager becomes clear after the first survey. European standard EN 13187 details thermographic control methods for the thermal properties of building envelopes.
Thermographic surveys reveal hidden issues—thermal bridges, poor insulation, air infiltration points. In practice, homeowners are often surprised by thermal imaging results, as problems appear in the most unexpected places.
Cost of Home Insulation and Investment Payback
How much does it cost to insulate a home in 2025? Investments range from $5,000 to $25,000, depending on the area and materials chosen. The average cost of home insulation is $150–$200 per square meter for external facade insulation.
Detailed cost and payback calculations help make informed decisions. Proper energy efficiency investments pay off quickly.
| Building Area | Insulation Type | Total Cost | Annual Savings* | Payback Period** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m² | Facade with mineral wool | $12,000 | $1,200–1,500 | 8–10 years |
| 150 m² | Comprehensive thermal protection | $20,000 | $2,200–2,800 | 7–9 years |
| 200 m² | Premium system | $35,000 | $3,500–4,200 | 8–10 years |
* Savings are based on a moderate climate with quality work
** Payback periods do not account for energy tariff inflation
These calculations highlight the economic appeal of thermal protection investments. Quality insulation, adhering to all technical requirements, pays off in 7–10 years and provides savings throughout its service life (20–50 years, depending on the material).
Can you insulate a home internally on a limited budget? Yes, but vapor barrier technologies must be followed. The cost of internal wall insulation is $80–$120 per square meter. The price per m² depends on the chosen technology and materials.
Start with Heat Loss Diagnostics
Want to know where your home is losing heat? Home energy audit services are provided by certified specialists. The average cost of diagnostics is $300–$500, but it will pinpoint exact heat loss locations and help plan the insulation budget effectively.
When choosing a contractor, pay attention to:
- Certificates for materials and work
- Portfolio of completed projects with measurable results
- At least 5-year warranties on insulation work
- Compliance with European quality and safety standards
Reducing heat loss in homes during winter is a strategic investment in comfort and savings for decades to come. A comprehensive approach to improving home energy efficiency, including thermal protection of all building elements with a continuous thermal envelope, modern windows, and heat recovery systems, can cut heating costs by 40–60% when all technical requirements are met. Well-executed insulation not only saves money but also increases property market value, creates a healthy indoor climate, and fully complies with European energy efficiency and fire safety standards.

