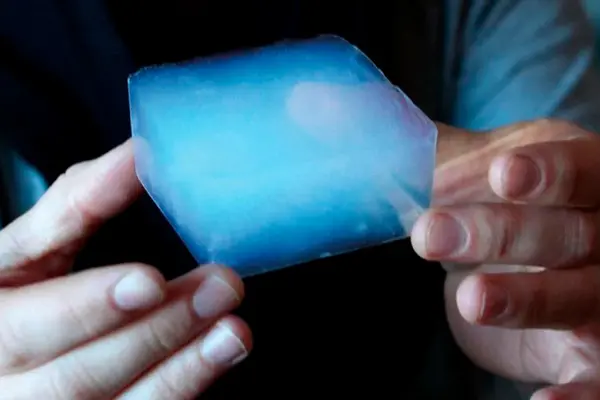
Aerogel — the material of the future. In 2025, this ultra-thin insulator is revolutionizing the construction industry thanks to its record-low thermal conductivity of 0.013-0.025 W/m·K. Imagine: a 5 mm thick sheet replaces 70 mm of mineral wool! Aerogel insulation, composed of 99% air, provides energy efficiency that architects and engineers could only dream of before.
What is aerogel: nanotechnology in construction
Aerogel — is frozen smoke. Not just a beautiful metaphor.
This nanoporous material is a gel where the liquid phase is completely replaced by gaseous through supercritical drying. It should be noted that sol-gel production technology allows creating a structure with pores sized 2-5 nm, making aerogel a unique thermal insulation solution. Mesoporous materials based on silicon dioxide demonstrate a density of only 1-150 kg/m³ with porosity of 95-99.8%.
"In one of the recent projects, using 10 mm thick aerogel instead of traditional 50 mm insulation allowed saving 40% of installation space without loss of thermal protection properties." — thermal engineer Mark Johnson, 15 years of experience in industrial construction.
Technical characteristics and properties of aerogel
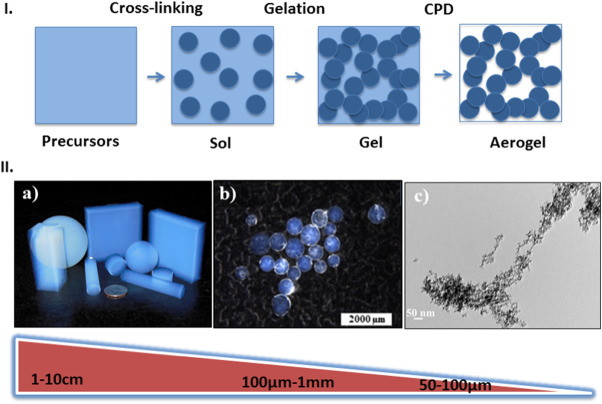 The thermal conductivity coefficient of aerogel is mind-boggling. The indicators impress even experts. Recent studies by Ákos Lakatos and his colleagues experimentally confirmed the unique thermal properties of aerogel coatings under real operating conditions.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of aerogel is mind-boggling. The indicators impress even experts. Recent studies by Ákos Lakatos and his colleagues experimentally confirmed the unique thermal properties of aerogel coatings under real operating conditions.
Comparative characteristics of various types of aerogel demonstrate the superiority of nanotechnologies over traditional insulators.
| Material type | Thermal conductivity, W/m·K | Density, kg/m³ | Temperature range, °C | Thickness, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz aerogel | 0.013-0.017 | 80-200 | -273 to +650 | 5-10 |
| Aerogel on glass fiber | 0.016-0.018 | 130-180 | -200 to +675 | 5-20 |
| Ceramic fiber + aerogel | 0.020-0.025 | 150-220 | -40 to +1000 | 10-25 |
| Mineral wool (comparison) | 0.035-0.045 | 30-200 | -180 to +400 | 50-200 |
The data shows that aerogel surpasses traditional materials in all key energy efficiency parameters. All specified characteristics comply with international standards ASTM C1728 and ISO 22482:2021 for aerogel insulation.
Hydrophobic insulation based on aerogel repels moisture by 99%, while remaining vapor permeable. It is known that this unique combination of properties makes the material ideal for humid climatic conditions. In practice working with industrial facilities, I often notice that non-combustible aerogel class A1 withstands direct flame exposure up to 1200°C without structural deformation.
Types of nano-insulation and application areas
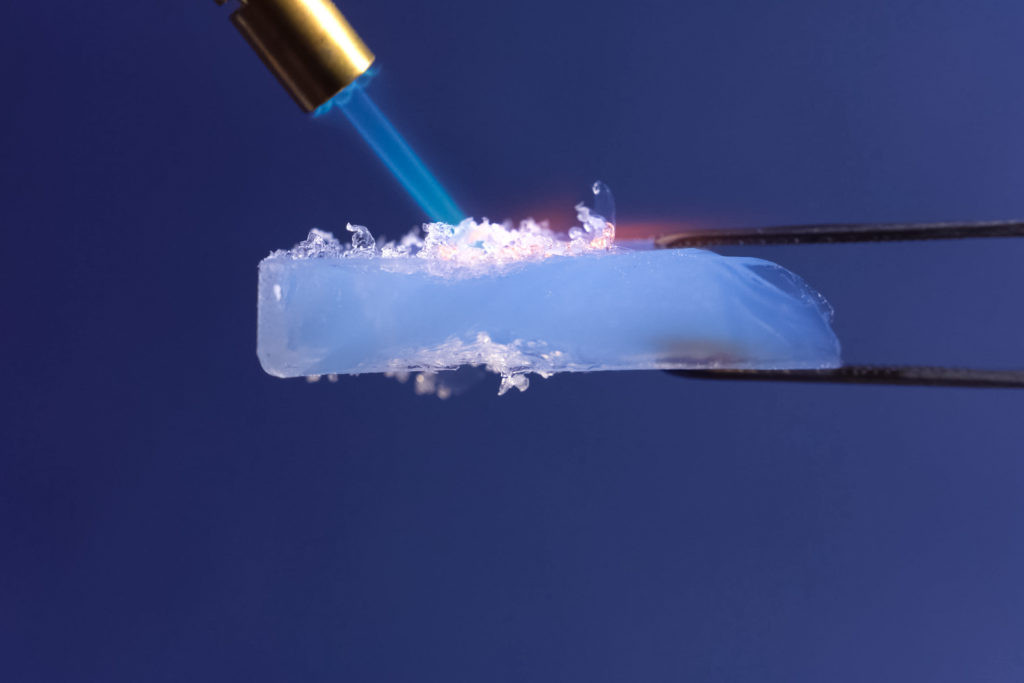 High-temperature insulation — is just one direction. Cryogenic technology opens new horizons. Where else is this amazing composition used?
High-temperature insulation — is just one direction. Cryogenic technology opens new horizons. Where else is this amazing composition used?
Quartz-based silica gel is used in building insulation where maximum energy efficiency with minimum thickness is required. Considering the design features of 2025 buildings, architects choose nanomaterials for facade insulation, roof thermal insulation, and floor insulation. At one of the facilities last season, using roll material allowed reducing installation time by 60% due to ease of installation.
"2024 studies conducted according to ISO 834 methodology showed that composites with 20-40% nanoparticle content maintain structural integrity under high temperature exposure for an hour without cracking." — results from building materials laboratory tests.
Industrial applications
Pipeline insulation at petrochemical plants requires compositions that withstand extreme loads. Nano-insulation handles tasks where conventional insulators are powerless: equipment insulation at temperatures up to +1000°C, personnel protection from thermal shock, industrial insulation in aerospace industry. Thus, the Guinness Book of Records includes this material for 15 parameters — truly unique indicators for the industry!
Aerogel production and technologies
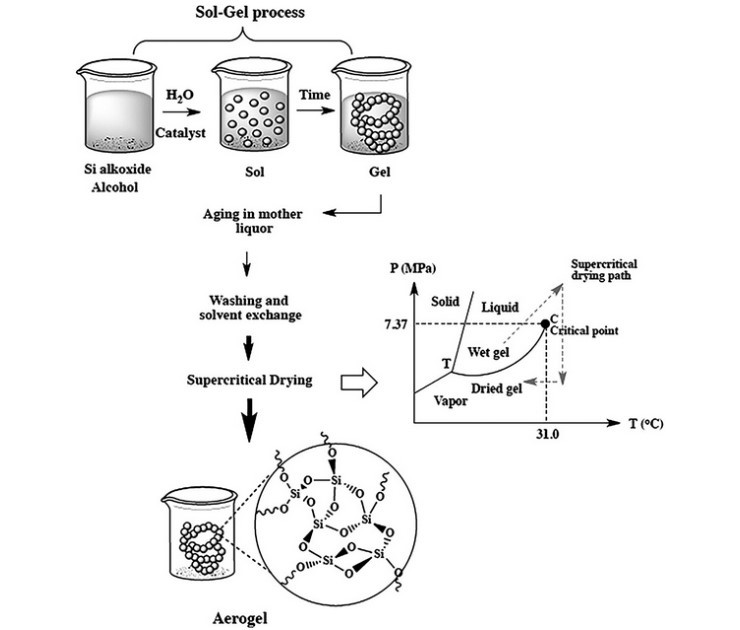 The process is complex. But revolutionary.
The process is complex. But revolutionary.
Sol-gel technology begins with creating a gel based on silicon nanoparticles, where each particle smaller than 5 nanometers forms the porous structure of the future material. Supercritical drying at temperature above the critical point of the solvent allows removing liquid without destroying nanopores. Detailed methods of silicon composition synthesis are described in scientific works by materials science specialists. This process, developed back in 1931 by Steven Kistler, is now improved to industrial scales.
"2025 production lines allow obtaining nano-insulation at a cost of $15-25 per square meter, making the material competitive with premium traditional-type insulators."
Nano-insulation prices in 2025
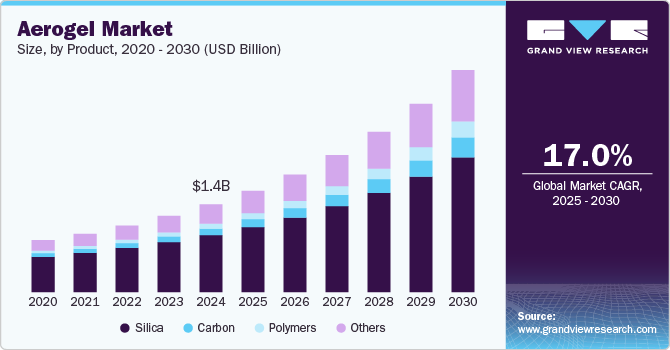 The cost varies from $25 to $120 per square meter depending on type and manufacturer. Simple payback calculation shows investment attractiveness.
The cost varies from $25 to $120 per square meter depending on type and manufacturer. Simple payback calculation shows investment attractiveness.
Basic grades cost $25-40/m², ceramic fiber with nano-additives — $50-80/m², premium segment reaches $120/m². In practice working with private clients, I notice: with 30-40% energy savings, the material pays back in 3-4 years in arctic conditions and 5-8 years in temperate climate. It should be considered that initial investments are quickly compensated by reduced heating bills.
Advantages and disadvantages of aerogel
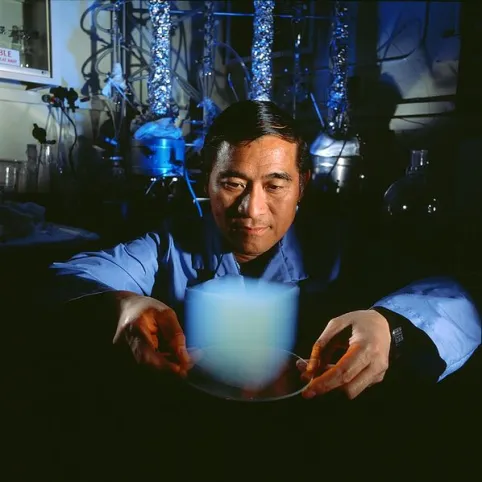 Like any nanotechnology, the composition has its features. Objective analysis will help make the right decision. Material safety is confirmed by multiple tests.
Like any nanotechnology, the composition has its features. Objective analysis will help make the right decision. Material safety is confirmed by multiple tests.
Advantages include heat conservation at the level of space technologies, space saving up to 80%, deformation resistance and service life over 20 years. In practice, I often observe that clients are surprised by the strength — commercial samples withstand loads 200-500 times their own weight. Used by NASA in Martian missions for thermal insulation and sample collection — proof of technology reliability!
Disadvantages include high initial cost and specific logistics requirements: the material requires careful transportation due to potential packaging fragility, delivery radius limitations from warehouses. Installation requires protective equipment. But these minuses are compensated by long-term energy savings and excellent operational parameters.
Comparing aerogel with innovative insulators
Nano-insulation versus mineral wool — is like a sports car versus a cart. The difference is colossal in all parameters. But how does the material relate to other high-tech solutions?
Insulation efficiency is 3-5 times higher than polyurethane foam indicators with half the thickness. Insulator comparison shows: where foam plastic requires 100 mm, ultra-thin composition needs only 20 mm for the same thermal protection. It is known that vacuum insulation demonstrates comparable thermal conductivity parameters (0.004-0.008 W/m·K), but loses in reliability — any damage to vacuum panel is critical, while nanomaterial retains properties even under mechanical impacts.
Space saving is critically important in 2025 construction, where every centimeter costs money. High-efficiency thermal insulation provides optimal balance between efficiency, reliability and durability among all high-tech insulation solutions.
Aerogel ecology and sustainability
In the era of green building, environmental parameters play a decisive role. Nano-insulation — champion of sustainable construction. Ecology is confirmed by independent studies.
Silicon composition is produced from natural quartz sand — one of the most common materials on Earth. Considering production design features, the material contains no toxic substances, emits no harmful vapors and is theoretically suitable for recycling, although industrial technologies are still in development. At the end of life cycle, composition can be crushed and used as filler for new composites or as adsorbent for water and air purification. Vapor-permeable insulator does not accumulate moisture, preventing mold and fungus development.
Carbon footprint is 2-8 kg CO₂ per kg of material by various estimates versus 4-6 kg for traditional insulators. Thus, production environmental footprint is compensated by energy savings in the first years of operation.
provides optimal balance between efficiency, reliability and durability among all high-tech insulation solutions.
Aerogel installation and mounting
 Aerogel installation is simpler than it seems. Material flexibility — its main advantage during mounting.
Aerogel installation is simpler than it seems. Material flexibility — its main advantage during mounting.
Aerogel mounting is performed with standard tools: material cuts easily, requires no special surface preparation, mounts at any temperature. According to ISO 22482:2021 standard requirements, when installing aerogel coatings it's important to use respiratory protection equipment, as with any fibrous materials. Considering design features, the standard prescribes compliance with conformity assessment procedures and proper product marking.
Prospects and technological trends
The market grows 11% annually. By 2030, volume will reach $2.5 billion. What technologies will determine the industry's future? The answer lies in next-generation materials science.
Graphene compositions with density 0.16 mg/cm³ have already surpassed silicon analogs in adsorption properties. Cellulose-based biomaterials are in research and development stage, opening the path to fully renewable insulation solutions. Thus, hybrid composites promise revolution in thermal energy storage systems. In one recent project, bio-nanocomposite application showed 60% carbon footprint reduction compared to traditional solutions.
Space technologies descend to Earth: research on promising properties for space applications is ongoing, and these developments will find application in extreme terrestrial conditions. Additive technologies allow printing complex geometry structures directly at construction sites. Innovative materials become reality today, offering energy-saving solutions that seemed like fantasy just a decade ago.

