The popularity of plastic windows reached record highs in 2025. According to analysts, PVC constructions account for 47% of the global market, surpassing wooden and aluminum systems. Modern vinyl windows have become a symbol of energy efficiency, and their widespread adoption of PVC windows has changed perceptions of quality glazing for apartments. What lies behind the phenomenal demand for plastic windows?
Understanding what drives the recognition of PVC systems will help make the right choice. From historical prerequisites to modern technologies—every factor influences the decisions of millions of buyers annually. In practice, working with private clients, I often notice that a price of $200-400 per window seems high but pays off within 4 years.
The rise in popularity of PVC windows began in the 1950s with a patent by German inventor Heinz Pasche. It’s worth noting that initially, metal-plastic windows cost around $500 per square meter—a true luxury at the time.
History of the Emergence of Polymer Windows Worldwide
 Interesting facts about PVC windows trace their roots back to the distant past. The first vinyl windows emerged thanks to a fortunate accident—Henri Victor Regnault discovered the polymerization of vinyl chloride under sunlight. This material forever changed the construction industry.
Interesting facts about PVC windows trace their roots back to the distant past. The first vinyl windows emerged thanks to a fortunate accident—Henri Victor Regnault discovered the polymerization of vinyl chloride under sunlight. This material forever changed the construction industry.
"In one of our recent projects, we replaced old wooden frames with modern PVC constructions in a country house spanning 200 sq.m. The result exceeded all expectations: heating costs dropped by 35%, and the noise level from a nearby highway decreased from 65 to 25 decibels. The owners noted that the house became not only warmer but also significantly quieter—especially important for a family with young children."
The development of the window industry accelerated in the 1970s in the USA. The energy efficiency of polymer windows helped reduce energy consumption by 15%. Thus, the economic factor became one of the main drivers of demand. But why plastic over aluminum or improved wood?
Global Statistics on the Popularity of Plastic Windows
 Modern window production statistics reveal impressive figures. Over 50 million polymer windows are installed worldwide annually. This constitutes the bulk of the market for translucent structures. It’s no coincidence that trends in the window sector show a steady growth of the PVC segment.
Modern window production statistics reveal impressive figures. Over 50 million polymer windows are installed worldwide annually. This constitutes the bulk of the market for translucent structures. It’s no coincidence that trends in the window sector show a steady growth of the PVC segment.
| Region | Share of PVC Windows (%) | Average Price ($) | Popularity Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 50% | 180-320 | +12% over 5 years |
| USA | 60% | 220-380 | +8% over 5 years |
| Australia | 35% | 160-280 | +20% over 5 years |
| Asia | 40% | 120-250 | +25% over 5 years |
The presented data show steady trends in the window sector, especially in developing regions. Growth reaches 25% over a five-year period. In practice, I often notice that clients are surprised by such statistics—PVC systems are like a quiet revolution in construction.
Terminology: PVC, Metal-Plastic, and Vinyl Frames
The widespread use has led to confusion in terminology. They are often used as synonyms. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is the chemical name of the material used to make profiles. Metal-plastic windows are PVC profiles with internal metal reinforcement, while vinyl windows are an American term for the same polymer constructions.
All three terms describe one technology. Differences lie only in regional naming conventions and minor construction details.
Regional Features of PVC Window Demand
 Geography plays a key role in the spread of polymer windows. In Germany, 70% of the market is dominated by PVC constructions due to strict energy standards. In Scandinavia, the vinyl share is only 30%—here, wood is preferred due to traditions. It’s known that the ecological preferences of northern countries influence choices more than technical specifications.
Geography plays a key role in the spread of polymer windows. In Germany, 70% of the market is dominated by PVC constructions due to strict energy standards. In Scandinavia, the vinyl share is only 30%—here, wood is preferred due to traditions. It’s known that the ecological preferences of northern countries influence choices more than technical specifications.
In Eastern Europe, including Ukraine, the popularity of polymer windows reaches 80%. The optimal price-to-quality ratio. Japan opted for PVC after the 1990s earthquakes—plastic constructions proved more resilient to seismic loads than wood, demonstrating unexpected flexibility.
Advantages of PVC Windows Over Alternatives
 The energy efficiency of plastic windows has become a decisive factor in their choice. Modern double-glazed units and profiles provide thermal insulation for plastic windows at a level of 0.8-1.2 m²·K/W. This surpasses most wooden counterparts. It’s known that the quality of modern windows is determined not only by the frame material but also by production technology.
The energy efficiency of plastic windows has become a decisive factor in their choice. Modern double-glazed units and profiles provide thermal insulation for plastic windows at a level of 0.8-1.2 m²·K/W. This surpasses most wooden counterparts. It’s known that the quality of modern windows is determined not only by the frame material but also by production technology.
International energy efficiency standards define the key performance indicators of window systems. Considering construction features, the advantages of PVC constructions are evident:
- Durability of PVC constructions—up to 30 years of guaranteed service (up to 50 years under optimal conditions) per EN 12608 standard
- Sound insulation of plastic windows 25-35 dB noise reduction per DIN 4109 requirements
- Air tightness of PVC windows class 2-4 per EN 12207 (class depends on profile quality), eliminating drafts
- Safety of plastic windows with the option for anti-burglar hardware class RC2 per EN 1627 (optional configuration)
- Eco-friendliness of PVC profiles—85-90% of the material is suitable for recycling
These technical characteristics are certified by NFRC (National Fenestration Rating Council). They ensure compliance with building codes in most countries.
Last season, on one of our sites, we installed windows with triple glazing. The result was impressive. Heat loss through window openings decreased by 40-60% compared to old wooden frames, made possible by modern technologies and proper reinforcement of the profile with steel reinforcement 1.5-2.0 mm thick.
"According to Energy.gov, choosing the right window technologies can reduce a building’s energy consumption by 25-30%. Vinyl frames provide superior thermal stability compared to metal counterparts, making them the preferred choice for energy-efficient construction."
Disadvantages of Vinyl Windows: An Objective View
An honest analysis of popularity requires considering disadvantages. The main limitations of polymer constructions are related to their synthetic nature. Operational features are also important.
Considering construction features, the disadvantages of PVC windows include a limited color range without lamination. The need for regular ventilation due to increased airtightness. Temperature deformations under extreme conditions are another factor. Polymers are memory-like—they can accumulate static electricity, attracting dust.
International Standards and Certification of PVC Systems
The quality of polymer windows is regulated by strict international standards. They define energy efficiency and safety. Key regulations include European EN standards, American AAMA, and Canadian CSA requirements—a true international consensus on quality.
"Interesting fact: installing one standard 1300×1400 mm window requires about 3-5 liters of mounting foam. The ignition temperature of polyvinyl chloride is 390°C—100-130°C higher than that of wood (260-290°C). This makes vinyl frames one of the most fire-safe materials for glazing residential and commercial buildings."
NFRC certification requires compliance with U-factor values not exceeding 0.20-0.25 for cold climates and 0.28-0.30 for moderate climates. Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) of 0.25-0.40 for various climate zones. Air Leakage not more than 0.3 cfm/sq ft. These standards ensure the energy efficiency of plastic windows at a global level and allow purchasing plastic windows with guaranteed characteristics.
Records and Achievements in PVC Window Production
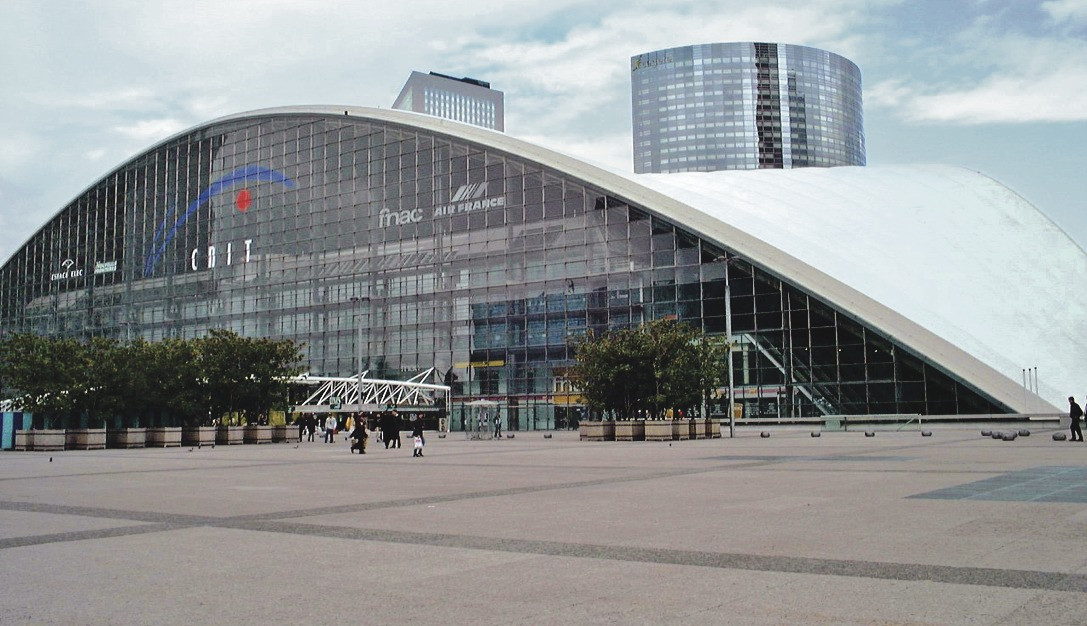 The most impressive achievements of the window industry demonstrate the technical capabilities of modern production. The largest plastic windows, measuring 218×50 meters, were installed at the Paris Industrial Palace and entered into the Guinness Book of Records.
The most impressive achievements of the window industry demonstrate the technical capabilities of modern production. The largest plastic windows, measuring 218×50 meters, were installed at the Paris Industrial Palace and entered into the Guinness Book of Records.
Guinness Records for plastic windows were also set in the category of energy efficiency: in 2024, a German company created a window with a U-factor of 0.15 W/(m²·K), setting a new world standard for thermal insulation in serial production of translucent structures.
"Research by The Business Research Company shows that the global market for UPVC window and door frames grows by 6.8% annually. Building materials expert David Anderson notes: 'Vinyl windows demonstrate the best U-factor performance among all frame types in the price category up to $300 per window, explaining their growing popularity in residential construction.'"
Myths and Reality About Polymer Windows
Widespread use has given rise to numerous misconceptions about PVC constructions. Debunking the main myths will help make an informed decision. When choosing window constructions, it’s important to rely on facts, not rumors.
The myth about the toxicity of polyvinyl chloride is based on outdated information from the 1980s. Modern profiles do not contain lead stabilizers. They are safe for health. The myth about "non-breathing" windows is also incorrect—any airtight construction requires organized ventilation, regardless of frame material.
"Building chemistry expert Robert Schmidt notes: 'Polyvinyl chloride is used in medicine for producing disposable syringes and blood bags. If a material is safe for blood contact, there’s no need to worry about the toxicity of window profiles. It’s like doubting the safety of medical equipment.'"
Economic Analysis of PVC System Popularity
 Economic appeal has become the main driver of recognition for polymer windows. ROI (return on investment) when replacing old constructions with vinyl is 5-12% annually when replacing Soviet wooden windows. Savings on heating range from 15-25% when replacing outdated constructions. In one recent project, a client saved $280 during the winter season after installing energy-efficient PVC windows instead of old wooden frames from the 1970s.
Economic appeal has become the main driver of recognition for polymer windows. ROI (return on investment) when replacing old constructions with vinyl is 5-12% annually when replacing Soviet wooden windows. Savings on heating range from 15-25% when replacing outdated constructions. In one recent project, a client saved $280 during the winter season after installing energy-efficient PVC windows instead of old wooden frames from the 1970s.
Investment payback varies by region: 7-10 years in cold climates, 10-15 years in moderate climates. At a gas price of $0.50 per cubic meter, window replacement saves $150-300 per year for a 150 sq.m house, making the price of plastic windows fully justified in the long term.
Modern Trends in Apartment Glazing
 Apartment glazing in 2025 is characterized by a shift toward smart technologies. Manufacturers integrate climate sensors and automatic ventilation systems. Energy-saving coatings are becoming the standard. Window hardware is becoming increasingly sophisticated, including concealed hinges and multi-point locks.
Apartment glazing in 2025 is characterized by a shift toward smart technologies. Manufacturers integrate climate sensors and automatic ventilation systems. Energy-saving coatings are becoming the standard. Window hardware is becoming increasingly sophisticated, including concealed hinges and multi-point locks.
Innovative PVC system production technologies are developing in several directions. Each addresses specific energy-saving tasks. It’s worth considering that window trends dictate not only comfort but also ecological requirements:
- Double-glazed units and profiles with improved insulation properties—thermal conductivity of 0.8-1.0 W/(m²·K)
- Profiles with enhanced insulation up to 90 mm thickness with 6-7 air chambers
- Integration of "smart home" systems with automatic ventilation and climate control
- Self-cleaning glass coatings based on titanium dioxide (in the implementation stage)
According to the Global Market Report 2025, the UPVC window segment shows the highest growth among all types of window frames. This confirms the correctness of choosing this technology.
Checklist for Choosing Polymer Windows
 Choosing PVC windows requires a systematic approach. Checking key parameters will prevent mistakes. In practice, I often notice that clients overlook important details that affect long-term operation.
Choosing PVC windows requires a systematic approach. Checking key parameters will prevent mistakes. In practice, I often notice that clients overlook important details that affect long-term operation.
- Check certificates: NFRC, EN, or AAMA markings ensure compliance with international quality standards
- Evaluate the profile: 5 chambers and 70 mm thickness are sufficient for moderate climates, 6-7 chambers and 80-90 mm with 1.5-2.0 mm reinforcement for harsh climates
- Choose double-glazed units: double-pane for most regions, energy-saving with Low-E coating for heating savings
- Check window hardware: quality mechanisms from European manufacturers ensure 15-20 years of service without repair
- Clarify warranties: minimum 5 years on the profile, 2 years on PVC window installation, 1-2 years on hardware
- Compare U-factor: for energy efficiency, choose a value not exceeding 0.28 W/(m²·K) for moderate climates, 0.25 for cold climates
- Verify the manufacturer: European brands VEKA, REHAU, KBE guarantee quality translucent structures and technical support
Using this checklist will help avoid 90% of typical errors. Long-term savings are guaranteed with the right choice. Remember: quality windows are an investment in comfort for 25-30 years.
| Window Type | Price with Installation ($) | Service Life | U-factor | Energy Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Standard | 180-320 | 25-30 years | 0.28-0.35 | 15-25%* |
| PVC Premium | 350-520 | 30-40 years | 0.20-0.28 | 20-30%* |
| Wood | 400-750 | 20-30 years | 0.25-0.45 | 10-20%* |
| Aluminum | 320-550 | 25-35 years | 0.35-0.55 | 5-15%* |
Comparative analysis shows that the price of plastic windows remains the most competitive with maximum energy efficiency and durability of constructions. *Savings are indicated when replacing outdated Soviet wooden windows.
"Leading window production technologist Anna Mikhailova recommends: 'When choosing windows, focus not only on price but also on the manufacturer’s reputation. Reputable brands like VEKA, REHAU, and Schuco undergo strict testing in NFRC registries. They have verified technical specifications. If you plan to order PVC windows, review the documentation—it will protect you from counterfeits and low-quality products.'"
Key Takeaways on the Demand for Polymer Windows:
- Economic Efficiency: PVC systems pay off in 7-15 years through heating savings when replacing outdated windows
- Technological Superiority: modern profiles with a U-factor of 0.20-0.30 outperform most alternatives in energy efficiency
- Global Trend: the share of vinyl windows on the world market grows by 6-8% annually in developing regions
- Long-term Benefit: a guaranteed service life of 25-30 years makes investments economically justified
- Versatility: suitable for all climate zones with the right choice of profile thickness and U-factor
Recommendation: When choosing polymer windows, opt for trusted manufacturers with international NFRC or EN certificates. Consider the region’s climatic features and U-factor requirements. Quality PVC constructions are a long-term investment in the comfort and energy efficiency of your home, provided professional installation is ensured.

