In any construction or renovation, it is impossible to do without cement mixtures. In 2025, prices for quality cement range from $80 to $120 per ton. Understanding cement characteristics and labeling will help save not only money but also prevent serious problems in the future. After all, properly selected cement with optimal technical characteristics is like a reliable skeleton for the entire construction organism. A poor choice will destroy all your plans.
According to statistics, about 65% of construction problems are related to the incorrect choice of cement. By the way, even professional builders sometimes get confused with numerous designations and characteristics. Let's understand the details!
What is Cement and Its Main Characteristics
.webp) Cement is a fine-grained binding powder with a gray shade. When interacting with water, it forms a ready-made cement mortar, which turns into a solid monolith when hardened. The chemical composition of Portland cement includes oxides of calcium, silicon, aluminum, and iron. In construction work, I have often noticed that the higher the quality and strength of cement, the more reliable the structure.
Cement is a fine-grained binding powder with a gray shade. When interacting with water, it forms a ready-made cement mortar, which turns into a solid monolith when hardened. The chemical composition of Portland cement includes oxides of calcium, silicon, aluminum, and iron. In construction work, I have often noticed that the higher the quality and strength of cement, the more reliable the structure.
Key characteristics of cement determine its suitability for specific construction tasks:
- Strength (grade or class)
- Hardening speed
- Frost resistance
- Water resistance
- Resistance to aggressive environments
- Cement density
These properties of cement depend on mineral additives and production technology. The most expensive cement is not always the best choice. But the right one.
«When choosing cement, pay attention not only to the grade but also to additional characteristics such as frost resistance and water resistance. For exterior work, especially in regions with cold climates, choose cement with high frost resistance of at least F100-F150», — advises Alexander Petrenko, a civil engineer with 15 years of experience.
Decoding Cement Labeling: System of Designations
On cement packaging, you can see various alphanumeric designations. M400, CEM II/A-S 32.5N, PC 500-D0 — these mysterious combinations contain important information about the composition and properties of the material. Honestly, even professionals sometimes get confused with these designations.
In Ukraine, two labeling standards are used: the old GOST 10178-85 and the new GOST 31108, which is closer to European standards EN 197. In the USA, ASTM C150 standards are used for Portland cement and ASTM C595 for mixed cements. Differences between standards of different countries are significant, but they are all aimed at ensuring the quality and safety of building materials.
Labeling According to the Old GOST 10178-85
Traditional labeling includes:
- Cement type (PC — Portland cement, SPC — slag Portland cement, etc.)
- Strength grade (M300, M400, M500, M600)
- Additive content (D0, D20, etc.)
- Special properties (SS — sulfate resistant, GF — hydrophobic, etc.)
For example, the designation PC 500-D0 means Portland cement grade 500 without additives. In the Kyiv office, I noticed that many contractors still prefer this marking due to its simplicity and clarity.
Labeling According to the New GOST 31108
The new standard uses the European designation system:
- CEM + Roman numeral (I-V) — cement type
- Letters A, B, or C — percentage of additives
- Letter designation of additives (S — slag, L — limestone, etc.)
- Strength class in MPa (32.5, 42.5, 52.5)
- Letter of hardening speed (N — normal, R — rapid)
For example, the marking CEM II/A-S 32.5N is decoded as Portland cement with slag additive (6-20%), strength class 32.5 MPa, normal hardening.
| Grade by GOST 10178-85 | Class by GOST 31108 | European Standard EN 197 | American Standard ASTM | Compressive Strength | Main Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC 300 | CEM I 22.5 | CEM I 22.5 | Type I (Low strength) | 22.5 MPa | Plastering work, screeds |
| PC 400-D0 | CEM I 32.5N | CEM I 32.5N | Type I | 32.5 MPa | Masonry mortars, foundations |
| PC 400-D20 | CEM II/A-S 32.5N | CEM II/A-S 32.5N | Type IP(MS) | 32.5 MPa | General construction work |
| PC 500-D0 | CEM I 42.5N | CEM I 42.5N | Type III | 42.5 MPa | High-strength structures |
| PC 500-D20 | CEM II/A-S 42.5N | CEM II/A-S 42.5N | Type IP(HS) | 42.5 MPa | Monolithic structures |
| PC 600 | CEM I 52.5N | CEM I 52.5N | Type III (HE) | 52.5 MPa | Special high-strength structures |
This comparative table will help to correlate cement designations according to different standards and select a material with suitable characteristics. Especially useful for international projects where materials from different manufacturers may be used.
Main Types of Cement and Their Characteristics
 Five main types of cement by composition determine their scope of application. Each type has its unique properties.
Five main types of cement by composition determine their scope of application. Each type has its unique properties.
CEM I (PC) — Portland Cement
Classic Portland cement contains a minimum of 95% clinker with the addition of up to 5% of secondary components. This pure cement composition is characterized by a high rate of strength gain. Within a day after installation, it reaches approximately 50% of its design strength.
Main applications:
- High-strength structures
- Precast reinforced concrete products
- Structures operated in aggressive environments
CEM II — Portland Cement with Mineral Additives
Contains from 6% to 35% of active mineral additives that improve certain characteristics of cement. Last season, I encountered an interesting situation: cement with limestone additive showed better workability during pool construction.
Varieties depending on additives:
- CEM II/A-S — with blast furnace slag additive (6-20%)
- CEM II/A-P — with pozzolana additive (6-20%)
- CEM II/A-L — with limestone additive (6-20%)
- CEM II/B-S — with increased slag content (21-35%)
CEM III (SPC) — Slag Portland Cement
Slag Portland cement contains a significant amount of granulated blast furnace slag (from 36% to 65%). It is distinguished by increased sulfate resistance and low heat emission during hardening.
Used for:
- Hydraulic structures
- Massive concrete structures
- Underground structures in soils with aggressive waters
«For foundation construction in conditions of aggressive groundwater, I always recommend CEM III or sulfate-resistant Portland cement. A small surcharge at the construction stage will help avoid serious problems in the future», — notes Elena Kovalchuk, expert on building materials.
CEM IV — Pozzolanic Cement
Contains natural or artificial pozzolanic additives (21-55%). Has increased water resistance and chemical resistance.
CEM V — Composite Cement
Includes a combination of various mineral additives. Properties depend on the specific composition and ratio of components.
The Influence of Additives on Cement Properties
Mineral additives in cement significantly affect its technical characteristics. D0 means no additives, and D20 means the presence of 20% additives in the composition. But what does this give in practice?
Main types of additives:
- Slags (S) — increase sulfate resistance and water resistance
- Pozzolans (P) — improve chemical resistance
- Limestones (L) — improve workability
- Fly ash (F) — reduces cost, improves workability
- Microsilica (MS) — significantly increases strength and density
The use of additives allows modifying cement properties for specific tasks. Not all. But many.
To prepare a quality cement-sand mortar, it is necessary to consider the type of additives in cement. The ratio of cement, sand, and additives for mortars should be properly selected. Many builders who have worked with different additives compare a properly selected mixture to a well-tuned musical instrument — each component must sound in harmony with others.
| Additive | Effect on Strength | Effect on Water Resistance | Frost Resistance | Special Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No additives (D0) | Maximum | Medium | Medium | High heat emission during hardening |
| Slag (up to 20%) | Slightly decreases | Increases | Increases | Improved sulfate resistance |
| Slag (20-35%) | Decreases | Significantly increases | Increases | Reduced heat emission |
| Pozzolan | Decreases in early stages | Significantly increases | Medium | High chemical resistance |
| Limestone | Slightly decreases | No changes | No changes | Improved workability |
| Microsilica | Significantly increases | Significantly increases | Significantly increases | Increased density and durability |
The table helps to understand how cement characteristics will change with the addition of various components. The choice of additives depends on the specific requirements for concrete for a particular project.
How to Choose Cement by Grade and Strength
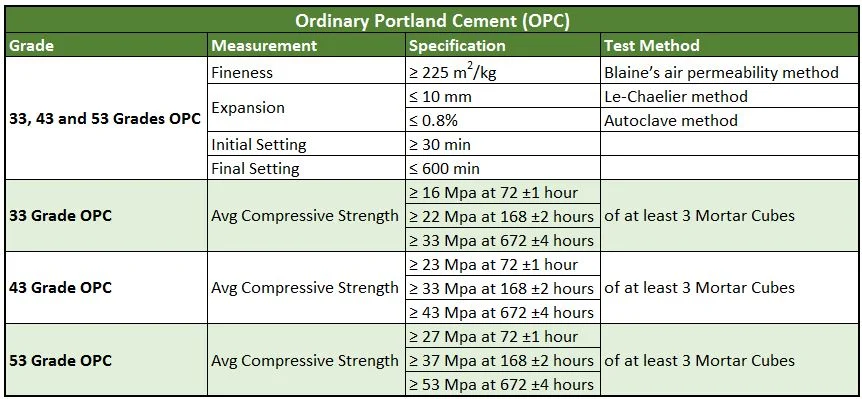 Strength is the key characteristic of cement. The strength class determines how much load the hardened cement composition can withstand.
Strength is the key characteristic of cement. The strength class determines how much load the hardened cement composition can withstand.
Main cement grades and their applications:
- M300 (22.5 MPa) — for interior finishing work, screeds, paving slabs
- M400 (32.5 MPa) — universal cement for most general construction work
- M500 (42.5 MPa) — for critical structures, foundations, reinforced concrete products
- M600 (52.5 MPa) — for particularly strong structures, bridges, high-rise buildings
When choosing cement, consider not only the strength grade but also the hardening speed. N — normal hardening, R — rapid hardening. The latter sets faster, which is important when working in cold weather or when early loading of structures is necessary.
When buying cement, pay attention to the storage conditions at the seller. At one site in Ternopil, there was a case when buying cement at an attractive price turned out to be a mistake — the material was stored in a damp room and partially lost its properties. After all, the use of cement for critical structures requires special attention to its quality.
«A story from one project: in 2018, our company was working on the construction of a residential complex in Kyiv. We purchased a large batch of M400 grade cement, not paying attention to the absence of D0 or D20 marking. After pouring the foundation, the concrete began to crack earlier than expected. Analysis showed a high content of additives that reduce frost resistance. We had to partially redo the work, which increased costs by 15%. Since then, we always carefully study the marking and require complete information about the composition from suppliers. This story taught us that knowledge of cement marking is not a formality, but a necessity for quality construction.»
How to Determine Cement Quality in Practice
 Determining cement quality is possible both in laboratory conditions and with simple practical tests. Approximately check. Not exactly.
Determining cement quality is possible both in laboratory conditions and with simple practical tests. Approximately check. Not exactly.
Laboratory tests of cement include:
- Determination of compressive and flexural strength
- Determination of setting times
- Checking the fineness of grinding
- Tests for cement frost resistance
- Measurement of physical characteristics of cement
Simple practical tests for application at the construction site:
- Visual assessment — quality cement has a uniform color without lumps and foreign inclusions
- Water test — a small amount of cement is mixed with water; quality cement sets and hardens quickly
- Shelf life check — cement absorbs moisture from the air over time and loses its properties
According to the Ukrainian Cement Manufacturers Association, about 15% of cement on the market does not meet the stated characteristics. In the experience of many builders, cement from a manufacturer with a good reputation costs $15-20 more, but saves thousands of dollars on subsequent repairs. Therefore, it is important to carefully choose suppliers.
Global Trends and Environmental Aspects of Cement Production
 Cement production is responsible for 7-8% of global CO₂ emissions. In 2025, environmental aspects of production are becoming increasingly important. Global cement production is about 4.1 billion tons, of which China produces more than 50%.
Cement production is responsible for 7-8% of global CO₂ emissions. In 2025, environmental aspects of production are becoming increasingly important. Global cement production is about 4.1 billion tons, of which China produces more than 50%.
Modern trends in cement production:
- Development of "green" cements with reduced carbon footprint
- Use of alternative energy sources in production
- Implementation of additives that improve environmental characteristics
- Increasing production energy efficiency
According to forecasts, by 2030, the demand for cement will grow by 12-15% due to urbanization and infrastructure projects, especially in Asia and Africa. In Ukraine, cement production in 2022 decreased by approximately 30% due to economic and military factors.
ASTM standards in the USA actively promote methods for testing and evaluating cement mixtures, ensuring their strength and safety, which is especially important when building in seismically active zones. And the World Economic Forum emphasizes the need to transition to more sustainable cement production to reduce global CO₂ emissions.

